Science of sleep cycles

Sleep isn’t one lengthy, uniform “off” state — it’s a repeating cycle of various brain-and-body modes that run all evening.
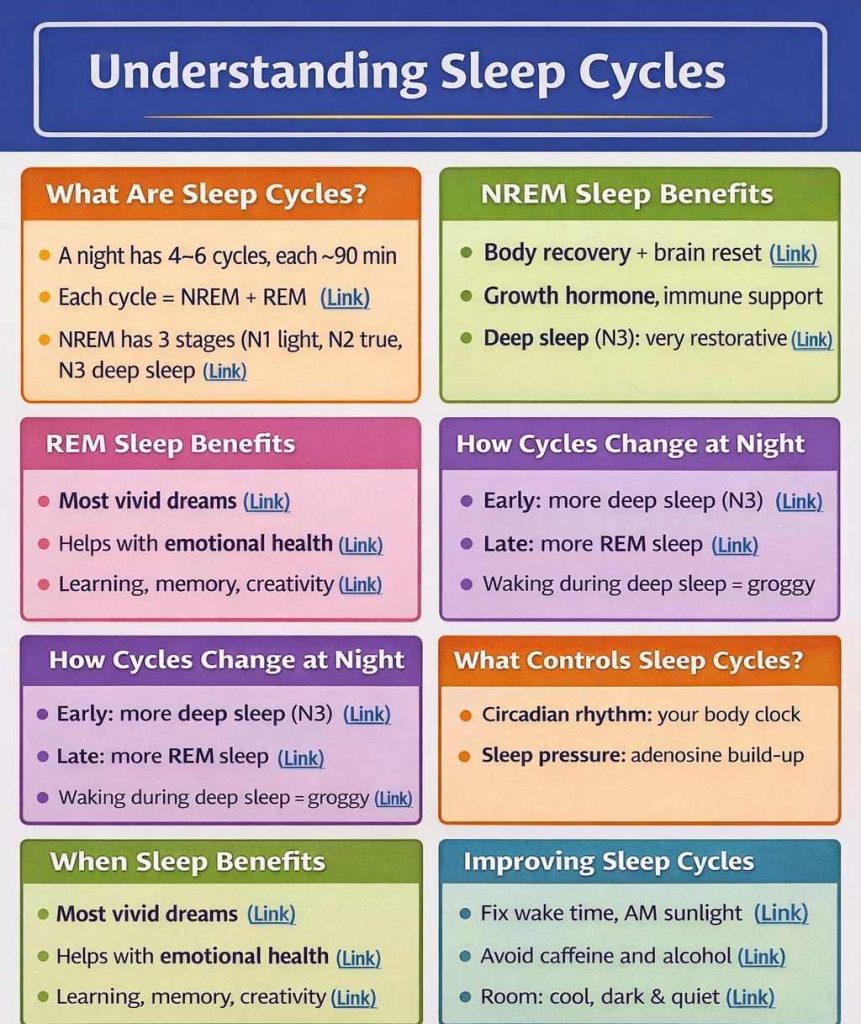
The fundamental concept
A typical evening is made from 4–6 sleep cycles, every lasting about 90 minutes (can vary ~70–110). Each cycle contains:
1) NREM sleep (Non-REM) — the “physique restore + mind reset” facet
This has 3 phases:
N1 (gentle sleep)
- You’re drifting out and in
- Simple to get up
- Mind begins slowing down
N2 (true sleep, nonetheless gentle)
- Your physique temperature drops
- Coronary heart charge slows
- Mind exhibits particular patterns known as sleep spindles and Okay-complexes
- This stage is the most important chunk of your evening (usually ~45–55%)
N3 (deep sleep / slow-wave sleep)
- Hardest to wake from
- Most bodily restoration occurs right here
- Progress hormone launch will increase
- Immune system help + muscle restore
- Crucial for feeling bodily refreshed
2) REM sleep — the “dream + emotional processing” facet
REM = Fast Eye Motion
- Most vivid goals occur right here
- Mind exercise seems to be nearer to being awake
- Muscle groups are largely “paralyzed” (so that you don’t act out goals)
- Necessary for reminiscence, studying, creativity, emotional regulation
How cycles change by the evening
Sleep cycles aren’t equivalent.
Early evening (first half)
- Extra deep sleep (N3)
- This is the reason going to mattress late can wreck restoration even when whole hours look okay
Late evening (second half)
- Extra REM
- This is the reason waking up early can have an effect on temper, focus, and emotional steadiness
Why you’re feeling groggy generally (sleep inertia)
If you happen to get up throughout deep sleep, you may really feel:
- heavy-headed
- confused
- drained even after “sufficient” hours
Waking nearer to gentle sleep or REM often feels simpler.
What controls your sleep cycles (the true science)
Two huge organic methods run your sleep:
1) Circadian rhythm (your physique clock)
- Managed by a mind space known as the SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus)
- Strongly influenced by gentle
- Helps determine when you’re feeling sleepy or alert
2) Sleep strain (adenosine build-up)
- The longer you keep awake, the extra adenosine builds up within the mind
- This creates a powerful drive to sleep
- Caffeine works by blocking adenosine receptors, not by giving “power”
Key hormones and chemical compounds concerned
- Melatonin: indicators nighttime (not a sleeping capsule, extra like a timing sign)
- Cortisol: naturally rises in early morning that will help you get up
- GABA: calming neurotransmitter, helps provoke sleep
- Orexin (hypocretin): retains you awake; low orexin is linked to narcolepsy
What sleep cycles are “for”
Totally different phases serve totally different jobs:
- Deep sleep (N3) → bodily restore, immune help, metabolic well being
- REM → emotional processing, reminiscence integration, creativity
- N2 → reminiscence consolidation + stabilizing sleep + studying motor abilities
Frequent myths (fast fixes)
❌ “Extra sleep is at all times higher”
High quality and timing matter. Oversleeping could make you’re feeling worse.
❌ “Dreaming solely occurs in REM”
You may dream in NREM too — REM goals are simply extra vivid.
❌ “Alcohol helps sleep”
It might probably knock you out, however it reduces REM and fragments sleep later.
Sensible ideas to enhance sleep cycles
In order for you higher cycles (not simply extra hours):
- Maintain a mounted wake time
- Get daylight inside 30–60 min of waking
- Keep away from caffeine 8–10 hours earlier than mattress
- Maintain room cool + darkish
- Don’t depend on alcohol for sleep
- Attempt to defend the final 2–3 hours of sleep (REM-heavy)
Fundamentals of Sleep Cycles
1) What’s a sleep cycle?
A sleep cycle is a repeating sample of sleep phases (NREM + REM) that sometimes lasts about 90 minutes.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
2) What number of sleep cycles do people have per evening?
Most adults have 4–6 cycles per evening relying on whole sleep time.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
3) How lengthy is one sleep cycle?
Normally 70–110 minutes, common round 90 minutes.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
4) What are the primary phases of sleep?
There are NREM (N1, N2, N3) and REM sleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/well being/sleep
5) What’s NREM sleep?
Non-REM sleep contains gentle sleep and deep sleep phases that restore the physique.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
6) What’s REM sleep?
REM is a stage the place mind exercise will increase and vivid dreaming is widespread.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
NREM Levels Defined
7) What’s N1 sleep?
N1 is the lightest stage the place you drift into sleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
8) What’s N2 sleep?
N2 is steady gentle sleep and makes up the most important portion of the evening.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
9) What’s N3 sleep?
N3 is deep sleep (slow-wave sleep), important for bodily restoration.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
10) Why is N3 known as “slow-wave sleep”?
As a result of EEG mind waves decelerate dramatically throughout this stage.
Hyperlink: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526132/
11) What occurs to coronary heart charge in NREM sleep?
Coronary heart charge and blood strain usually lower.
Hyperlink: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/well being/sleep
12) What occurs to inhaling NREM sleep?
Respiration turns into slower and extra common.
Hyperlink: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/well being/sleep
REM Sleep Defined
13) Why do eyes transfer in REM sleep?
REM contains speedy eye actions linked to energetic mind processing.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
14) Why does the physique get paralyzed in REM?
To forestall performing out goals (REM atonia).
Hyperlink: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526132/
15) Is REM sleep needed?
Sure—REM helps reminiscence, studying, and emotional regulation.
Hyperlink: https://www.well being.harvard.edu/newsletter_article/sleep-and-mental-health
16) When do you get most REM sleep?
Within the second half of the evening.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
17) Does REM sleep imply you might be sleeping evenly?
REM is “energetic sleep,” however waking from it’s usually simpler than deep sleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep
Sleep Structure (Evening Sample)
18) What’s sleep structure?
It’s the construction of sleep phases throughout the evening.
Hyperlink: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526132/
19) Why is deep sleep extra widespread early within the evening?
Sleep strain is highest early, so the mind prioritizes N3.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works
20) Why is REM sleep extra widespread late within the evening?
Circadian rhythm will increase REM tendency towards morning.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works
21) What’s sleep effectivity?
It’s the % of time in mattress truly spent sleeping.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-hygiene/sleep-efficiency
22) Is it regular to get up briefly at evening?
Sure. Quick awakenings are widespread and infrequently forgotten.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works
Mind Exercise and Sleep Science
23) What are sleep spindles?
Quick bursts of mind exercise in N2 linked to studying and reminiscence.
Hyperlink: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4636982/
24) What are Okay-complexes?
Massive EEG waves in N2 which will defend sleep from disturbances.
Hyperlink: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526132/
25) Why does the mind “clear itself” throughout sleep?
The glymphatic system will increase waste clearance throughout sleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/how-sleep-clears-brain
26) Which sleep stage is finest for reminiscence?
Each NREM (particularly N2/N3) and REM help several types of reminiscence.
Hyperlink: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3768102/
Desires and Sleep Cycles
27) Do goals solely occur in REM?
No. Desires can occur in NREM too, however REM goals are vivid.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/goals
28) Why are REM goals extra vivid?
REM mind exercise is nearer to wakefulness.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/goals
29) Why can we overlook goals?
Reminiscence methods are altered throughout REM and waking interrupts recall.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/goals/why-do-we-forget-dreams
30) What’s lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is being conscious you might be dreaming whereas asleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/goals/lucid-dreaming
Circadian Rhythm and Timing
31) What controls the physique clock?
The SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus) within the mind.
Hyperlink: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519507/
32) How does gentle have an effect on sleep cycles?
Morning gentle strengthens circadian rhythm; late gentle delays sleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/circadian-rhythm/light-and-sleep
33) What’s melatonin?
A hormone that indicators “nighttime” to the mind.
Hyperlink: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/well being/melatonin-what-you-need-to-know
34) Is melatonin a sleeping capsule?
Not precisely. It helps with timing greater than sedation.
Hyperlink: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/well being/melatonin-what-you-need-to-know
Sleep Strain and Chemical substances
35) What’s adenosine?
A mind chemical that builds up whereas awake and will increase sleepiness.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works/adenosine-and-sleep
36) How does caffeine have an effect on sleep cycles?
It blocks adenosine receptors and may scale back deep sleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/diet/caffeine-and-sleep
37) How lengthy earlier than mattress do you have to cease caffeine?
Usually 8–10 hours earlier than mattress (varies by individual).
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/diet/caffeine-and-sleep
Sleep Issues and Cycle Disruption
38) What’s sleep fragmentation?
Frequent awakenings that disrupt sleep phases and restoration.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works
39) What’s insomnia?
Issue falling asleep, staying asleep, or getting restorative sleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/well being/insomnia
40) Does stress have an effect on sleep cycles?
Sure, stress raises arousal hormones and reduces deep sleep.
Hyperlink: https://www.apa.org/matters/stress/sleep
41) How does alcohol have an effect on sleep cycles?
Alcohol reduces REM and causes extra awakenings later.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/diet/alcohol-and-sleep
42) How does smoking have an effect on sleep?
Nicotine is stimulating and may scale back sleep high quality.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/physical-health/smoking-and-sleep
43) How does sleep apnea have an effect on sleep cycles?
It repeatedly interrupts respiration and fragments deep sleep and REM.
Hyperlink: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/well being/sleep-apnea
Sleep Cycles by Age and Way of life
44) Do sleep cycles change with age?
Sure. Deep sleep tends to lower with age.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works/how-much-sleep-do-we-need
45) Why do youngsters sleep late?
Their circadian rhythm shifts later throughout puberty.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/teens-and-sleep
46) Why do older adults get up earlier?
Circadian rhythms usually shift earlier with age and sleep turns into lighter.
Hyperlink: https://www.nia.nih.gov/well being/sleep
47) Does train enhance sleep cycles?
Sure—common train can enhance deep sleep and sleep effectivity.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/physical-health/exercise-and-sleep
Monitoring Sleep Cycles
48) Can smartwatches precisely observe REM and deep sleep?
They estimate phases utilizing motion + coronary heart charge; accuracy is proscribed vs lab testing.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-studies/how-accurate-are-sleep-trackers
49) What’s the gold normal for measuring sleep phases?
Polysomnography (PSG) in a sleep lab.
Hyperlink: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-studies/polysomnography
50) What’s the finest “ideally suited” sleep sample?
A constant schedule with sufficient whole sleep so that you get each deep sleep and REM.
Hyperlink: https://www.cdc.gov/sleep/about_sleep/how_much_sleep.html

