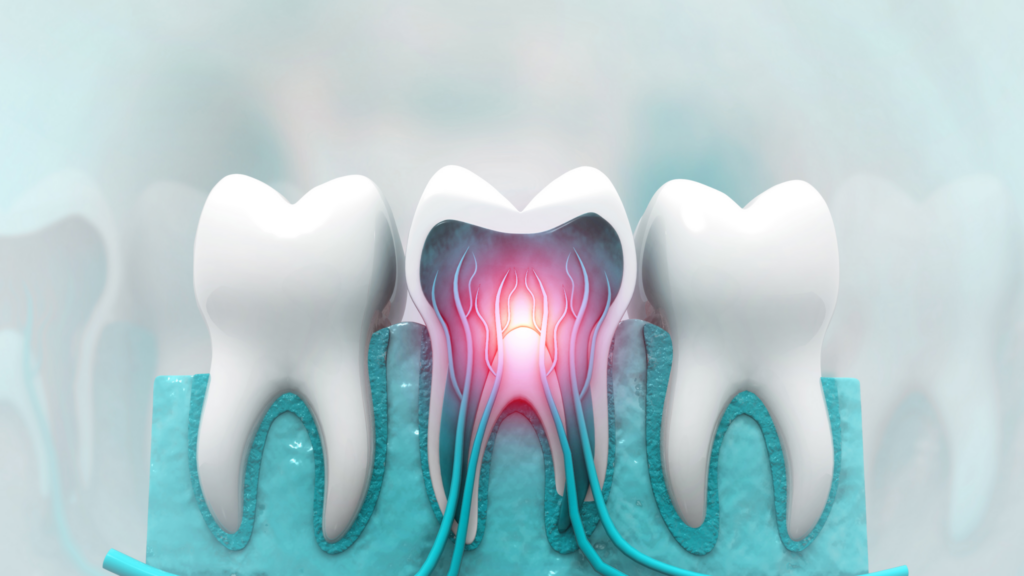
A new College of Michigan examine has discovered that tooth nerves are extra than simply ache detectors — additionally they play a protecting position that might have main implications for future dental remedies and improvements.
“After we take into account regenerating a tooth pulp, we have to deliver again the nerves.”
In a peer-reviewed paper printed in Cell Stories, researchers confirmed that sensory neurons in mice enamel are “multitaskers.” These nerves can set off a jaw-opening reflex inside milliseconds to stop additional harm or injury.
“We suspected there was a extra basic position for tooth nerves,” stated senior creator Dr. Joshua Emrick, assistant professor on the U-M College of Dentistry. “After we take into account regenerating a tooth pulp, we have to deliver again the nerves.”
‘Research challenges the prior assumption’
Utilizing superior reside imaging and behaviour-tracking instruments, the analysis workforce — made up of scientists from U-M’s departments of sensory neuroscience, dentistry and mechanical engineering — revealed that sensory neurons do greater than detect ache. They actively monitor each the internal pulp and the outer enamel of the tooth.
By making use of direct power to mouse enamel, the researchers examined the operate of particular myelinated sensory neurons. They used genetic labelling methods involving S100b and Scn10a — markers of myelinated somatosensory neurons — to uncover the position of intradental high-threshold mechano-nociceptors (HTMRs). In less complicated phrases, these are extremely specialised neurons that detect harmful mechanical forces and alert the mind in time to set off protecting reflexes.
“Our examine challenges the prior assumption that nerves contained in the tooth primarily operate to elicit ache and power us straight to the dentist for assist,” Emrick stated. “Should you’ve ever unintentionally bitten down in your fork, you’ve most likely skilled a startling jolt, but additionally stopped wanting fracturing your enamel. You might thank these intradental HTMRs for that.”
Learn associated article: Our Accountability: The Trigeminal Nerve
Learn associated article: Failed Mandibular Anaesthesia: Aberrant Nerve Pathways
Nerves sign motion in milliseconds
The workforce noticed that inside 5 to fifteen milliseconds of HTMR activation, a speedy jaw-opening reflex happens — lengthy earlier than the aware expertise of ache kicks in. This automated response helps forestall tooth fractures or deeper injury.
The findings problem long-held assumptions that nerves contained in the tooth primarily exist to trigger ache and immediate visits to the dentist.
Implications for tooth regeneration
The examine provides to a rising physique of analysis on tooth innervation.
Learn associated article: Tufts researchers develop ‘good’ dental implant to imitate pure enamel — subsequent step, testing the mind
The researchers are actually exploring what occurs after HTMRs are activated, together with long-term responses and potential purposes in regenerative dentistry.

