A Bluetooth-enabled versatile sensor patch from RMIT lets docs and sufferers see inside a therapeutic wound with out lifting the dressing, recognizing issues early, and maintaining restoration on monitor.
 Examine: Multiplexed Cutaneous Wound Monitor for Level-of-Care Functions. Picture credit score: New Africa/Shutterstock.com
Examine: Multiplexed Cutaneous Wound Monitor for Level-of-Care Functions. Picture credit score: New Africa/Shutterstock.com
Researchers on the Royal Melbourne Institute of Know-how (RMIT), Australia, developed a wearable wound monitoring system to ease power wounds and infections by decreasing the necessity for frequent bodily contact. An in depth report is printed in Superior NanoBiomed Analysis.
Background
Wearable wound screens are medical gadgets used for steady monitoring of wound therapeutic development. These gadgets are gaining appreciable consideration in healthcare sectors on account of their potential to supply an enormous quantity of helpful information to healthcare professionals and cut back the necessity for frequent consultations.
Wearable wound screens comprise a variety of refined sensors and complicated algorithms, which assist quantify numerous parameters, together with wound-site temperature, humidity, strain, and particular wound mattress biomarkers. This info helps healthcare professionals consider the progress of wound therapeutic and facilitate their wound care and treatment-related decision-making.
With the rising recognition of wearable wound screens, the RMIT researchers developed a multiplexed cutaneous wound monitor utilizing a “triangulated” strategy with superior built-in sensor expertise to trace numerous biomarkers and biophysical parameters associated to wound well being and research how these parameters work together with one another.
The wearable wound monitoring system
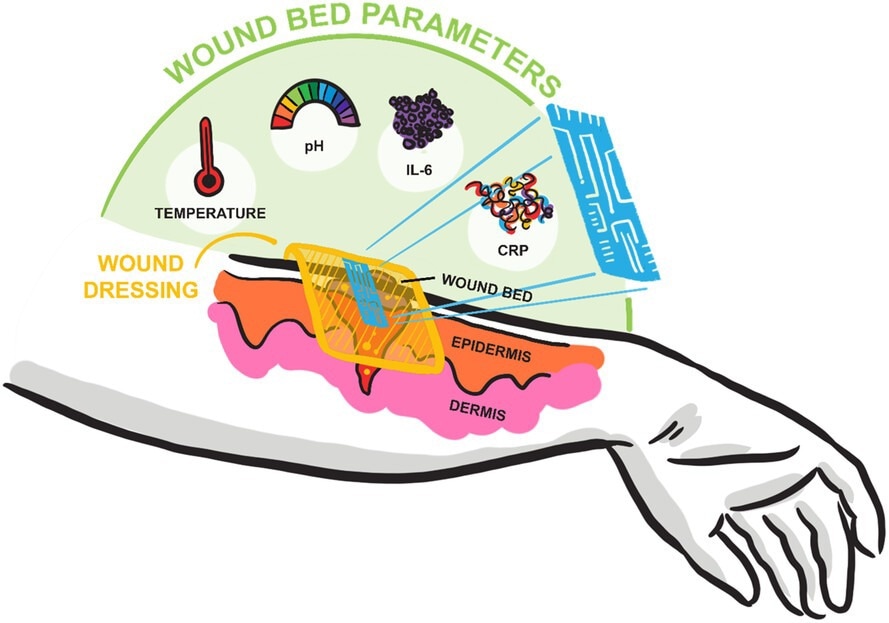
This versatile, reusable wound monitoring system comprises high-resistive silicon (HR-Si) conductometric biosensors to detect inflammatory biomarkers, a potentiometric pH sensor, and a temperature sensor. Bluetooth can be integrated to transmit information remotely for studying through an Android smartphone app (“FMM Join”). This would scale back the necessity for frequent dressing removing and bodily contact with the wound.
The researchers centered on two inflammatory biomarkers: interleukin 6 (IL-6) and C-reactive protein (CRP). These biomarkers play essential roles in wound therapeutic. IL-6 is launched within the preliminary section of wound trauma to advertise tissue restore by releasing proinflammatory cytokines. CRP, in flip, induces phagocyte-mediated destruction of lifeless cells and pathogens, thereby selling tissue restore.
The opposite two sensors had been used to repeatedly monitor the modifications in two very important biophysical parameters on the wound website, i.e., excessive temperatures indicating irritation or an infection, and pH modifications indicating totally different levels of wound therapeutic. Regular vs. irregular thresholds for these parameters had been outlined within the research; for instance, IL-6 < 45 nM and CRP < 40 nM point out regular therapeutic, whereas IL-6 > 45.36 nM and CRP > 41.67 nM recommend power an infection. Equally, a pH above 7.4 or a temperature above 38 °C can point out an infection or necrosis.
The researchers integrated these sensors on a system-on-chip platform enabled with Bluetooth expertise, which interfaces with a custom-developed telephone software.
Useful validation
The researchers examined the monitor’s performance by simulating circumstances within the laboratory and demonstrating match and suppleness by inserting the monitor on a human arm to indicate that it conforms effectively to the curved floor.
Because the researchers acknowledged, one benefit of the monitor is that its versatile sensors will be positioned on or subsequent to a wound beneath dressings. Their flexibility makes them adaptable to totally different wound shapes and physique areas.
For inflammatory biomarker monitoring, the sensors had been immobilized with CRP and IL-6 antibodies after which CRP and IL-6 antigens, respectively, for particular measurements. Any modifications within the ranges of inflammatory biomarkers in response to wound trauma had been indicated by the share change within the resistance of the sensors, which correspond within the app to respective modifications in voltage values in mV.
For temperature monitoring, the sensor response was measured as a change in output voltage to a change in temperature. The output voltage decreases with growing temperature.
The sensors had been hydrated for pH monitoring to enhance floor activation, and open circuit voltage measurements had been taken for the sensor over a broad vary of pH. Furthermore, temperature-dependent pH measurements had been carried out, displaying that the potential will increase correspondingly with growing temperatures. This allowed the group to evaluate interdependence between pH modifications and biomarker responses.
Utility and significance
The research gives proof-of-concept of a wearable wound monitoring system enabled with wi-fi Bluetooth expertise. The system reveals excessive effectivity in repeatedly monitoring modifications in inflammatory biomarker ranges, pH, and temperature on the wound website, that are essential in understanding the development of wound therapeutic.
About 500,000 Australians are affected by power wounds, which collectively price the nationwide healthcare system round $3 billion annually. Globally, the issue impacts thousands and thousands of sufferers.
This low-cost system may very well be a extra sensible various to disposable good bandages and different digital well being merchandise. It might tackle a widespread healthcare problem, notably for sufferers with power wounds. The electronics module is reusable, whereas the HR-Si and pH sensors are designed to get replaced with every dressing change.
The HR-Si-based sensor expertise used within the system has already been utilized to different medical gadgets to detect a number of biomarkers.
Total, the research highlights the system’s applicability in remotely monitoring the phases of wound therapeutic in actual time. Because the researchers talked about, future research might goal to develop a digital software tuned to every sensor individually, providing information visualization with an improved consumer interface.
The authors additionally word that the strategy may very well be tailored for different point-of-care diagnostic purposes by integrating extra biomarker sensors.

