New analysis reveals that social isolation and stress in the course of the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the ageing of the brains of older adults, no matter whether or not they contracted the virus, highlighting the pressing want for protecting methods past an infection management.
 Research: Accelerated mind ageing in the course of the COVID-19 pandemic. Picture Credit score: Shyntartanya / Shuttertock
Research: Accelerated mind ageing in the course of the COVID-19 pandemic. Picture Credit score: Shyntartanya / Shuttertock
In a latest examine revealed within the journal Nature Communications, a bunch of researchers examined whether or not the coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, with or with out extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) an infection, accelerated organic mind ageing in middle-aged and older adults.
The examine sought to differentiate the impression of an infection itself from the consequences of pandemic-related social disruption on mind ageing.
Background
Each three seconds, somebody worldwide develops dementia, but scientists nonetheless debate what hastens cerebral ageing. The appearance of COVID-19 raised issues, as SARS-CoV-2 impacts each grey matter (GM) and white matter (WM) on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). But tens of millions who by no means caught the virus endured isolation and missed care throughout lockdowns, stressors that additionally erode mind resilience.
Cross-sectional snapshots lack pre-pandemic baselines, making it unattainable to differentiate between organic and social harm. Figuring out the first driver is essential for predicting dementia and informing protecting insurance policies. The complexity of psychological well being outcomes in the course of the pandemic, together with variable findings throughout populations, has additionally made interpretation difficult.
Additional analysis is required to make clear causality and determine modifiable threat components for ageing populations worldwide.
In regards to the examine
Investigators mined the UK Biobank (UKBB), a cohort with multimodal MRI. Separate GM and WM mind age fashions have been educated on 15,334 wholesome adults scanned earlier than March 2020. From 1,865 imaging-derived phenotypes (IDPs) summarizing construction, diffusion, and T2 alerts, principal element evaluation (PCA) extracted 50 parts. Elastic web regression precisely predicted chronological age, yielding a imply absolute error (MAE) of practically three years; test-retest reliability was demonstrated by an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.98.
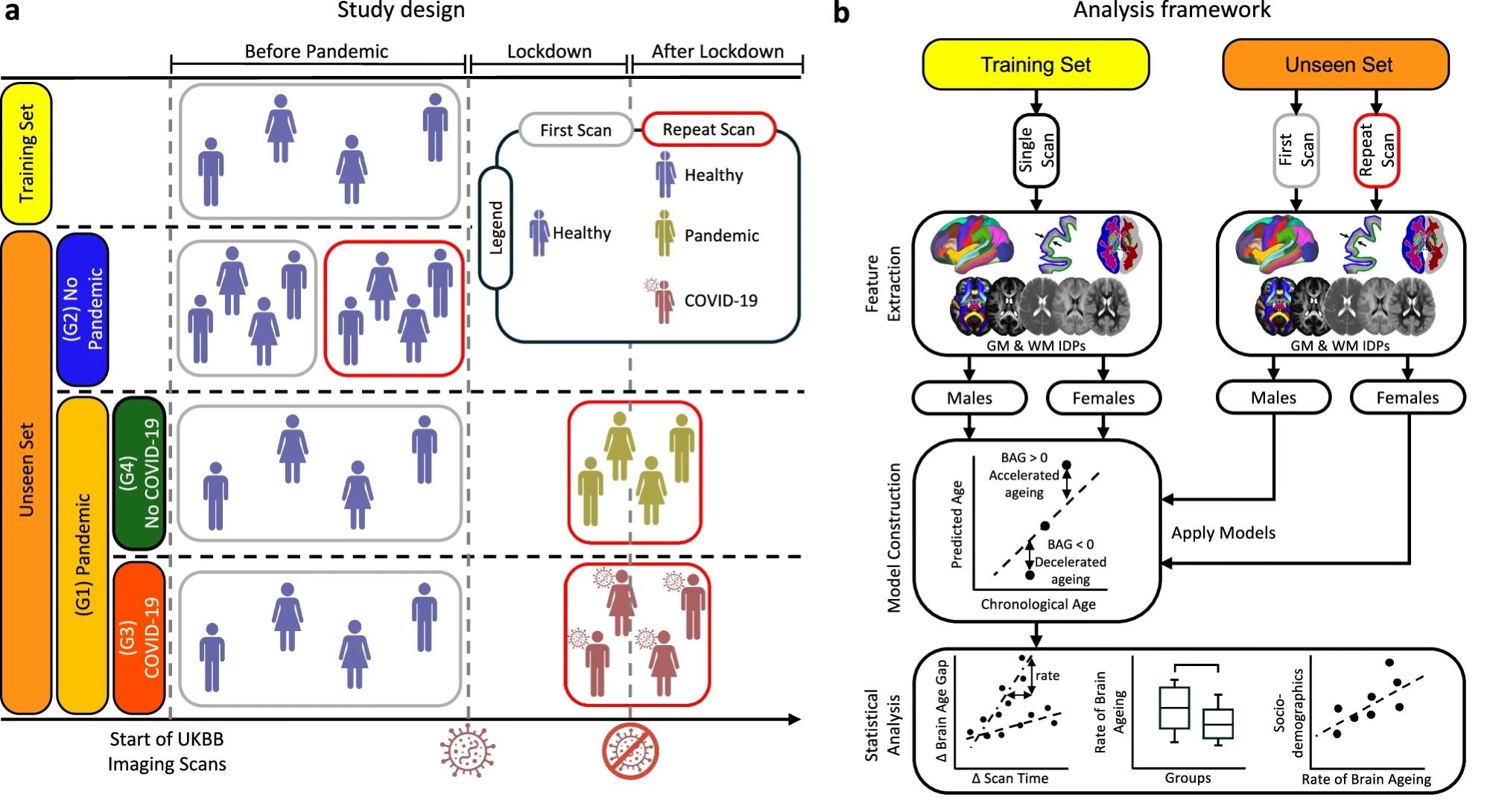 a A mind age prediction mannequin was educated utilizing 20-fold cross-validation on wholesome members with a single pre-pandemic scan (coaching set). The mannequin was utilized to an unseen set comprising the Pandemic group (G1) and the No Pandemic group (G2). G1 was additional subdivided into Pandemic–COVID-19 (G3) and Pandemic–No COVID-19 (G4). b Imaging-derived phenotypes (IDPs) have been extracted from gray matter (GM) and white matter (WM) throughout scan occasions. Separate prediction fashions have been educated by tissue sort and intercourse utilizing pre-pandemic information, after which utilized independently to scans from totally different time factors to estimate mind age hole (BAG). Statistical analyses assessed pandemic- and infection-related results utilizing longitudinal information.
a A mind age prediction mannequin was educated utilizing 20-fold cross-validation on wholesome members with a single pre-pandemic scan (coaching set). The mannequin was utilized to an unseen set comprising the Pandemic group (G1) and the No Pandemic group (G2). G1 was additional subdivided into Pandemic–COVID-19 (G3) and Pandemic–No COVID-19 (G4). b Imaging-derived phenotypes (IDPs) have been extracted from gray matter (GM) and white matter (WM) throughout scan occasions. Separate prediction fashions have been educated by tissue sort and intercourse utilizing pre-pandemic information, after which utilized independently to scans from totally different time factors to estimate mind age hole (BAG). Statistical analyses assessed pandemic- and infection-related results utilizing longitudinal information.
The fashions have been utilized to 996 volunteers, who underwent two MRI periods. Controls (n = 564) have been scanned twice earlier than the pandemic, whereas the pandemic cohort (n = 432) underwent one pre- and one post-restriction scan; 134 of them had laboratory-confirmed coronavirus illness 2019. Of the COVID-19 instances, solely 5 out of 134 members (<4%) required hospitalization, indicating that the cohort was nearly solely comprised of gentle instances.
Teams have been balanced for demographics, physique mass index, vascular threat, schooling, revenue, and deprivation rating. Solely inter-scan intervals ≥ 24 months have been accepted to scale back noise. An adjustment for the inter-scan interval was included to attenuate confounding by time between scans.
The first endpoint was the speed of change in mind age hole (RBAG), calculated as RBAG = ΔBAG / Δtime (months per yr). Permutation-based evaluation of variance with false discovery fee (FDR) correction was used to check the consequences of pandemic publicity, an infection standing, intercourse, chronological age, and socioeconomic adversity. All MRI acquisitions used an identical Siemens scanners and standardized protocols throughout 4 websites.
Research outcomes
The expected mind age on the first MRI session was statistically indistinguishable among the many three cohorts, together with pre-pandemic controls, pandemic members with out SARS-CoV-2, and pandemic members with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19, confirming a balanced baseline neuroanatomy. When the identical volunteers returned a median of two.7 years later, the brains of people that had lived by way of lockdowns seemed to be extra superior in age.
After adjusting for inter-scan interval, intercourse, physique mass index, and cardiovascular threat, their brains seemed 5.5 months older than these of controls, yielding Cohen d values of 0.61 for GM and 0.70 for WM.
Importantly, SARS-CoV-2 an infection itself didn’t account for the surge in instances. Pandemic volunteers who by no means caught the virus aged on the identical tempo as their contaminated friends, and each subgroups differed considerably from controls as soon as FDR correction was utilized.
Chronological age amplified vulnerability, as in controls, with every birthday including about three mind age days. Nonetheless, beneath pandemic situations, the slope greater than doubled to seven days in GM and eight days in WM; the variety of contaminated people elevated to just about ten days per calendar yr. Because the overwhelming majority of infections have been gentle, the examine couldn’t robustly assess whether or not illness severity (e.g., hospitalization or symptom length) modulated RBAG.
Intercourse variations have been evident, as beneath an identical pandemic publicity, male brains aged 33% quicker than feminine brains in GM; for WM, the distinction was related in sample however didn’t attain statistical significance. The interplay for intercourse was important for GM (FDR p = 0.008), however not for WM.
Socioeconomic adversity additional widened the hole. Individuals reporting low employment safety, poor self-rated well being, or low family revenue amassed between 1.5 and 5.8 extra months of mind ageing throughout follow-up relative to probably the most advantaged friends, and interplay phrases between deprivation indices and pandemic standing remained important.
Cognitive change was selective relatively than international. Customary reminiscence and language scores stayed secure throughout teams, but solely volunteers who skilled COVID-19 displayed slower Path Making Take a look at (TMT) efficiency.
Completion occasions elevated by 6–9% for numeric (TMT A) and alternating alphanumeric (TMT B) variations, and better RBAG correlated with slower TMT A pace (r = 0.23, p = 0.004), indicating that infection-associated neuroinflammation might doubtlessly convert silent structural vulnerability into measurable govt decline.
It must be famous, nevertheless, that the examine demonstrates affiliation relatively than confirmed causation on this mechanistic hyperlink.
BAG estimates remained orthogonal to chronological age; the test-retest ICC stayed 0.98; and MAE for age prediction by no means exceeded 3.1 years. Combined results fashions that concurrently entered deprivation, intercourse, an infection standing, and chronological age nonetheless attributed a considerable proportion of defined RBAG variance to pandemic publicity (roughly 46%, as per supplementary information), underscoring the dominant function of social disruption.
Continued follow-up will reveal whether or not the noticed structural shifts endure or reverse as regular social actions resume.
The examine authors word that longer-term follow-up and extra information, together with extra direct measures of psychological stress, are wanted to make clear the persistence and mechanisms of those results.
Conclusions
To summarize, the COVID-19 period accelerated organic mind ageing by roughly half a yr in beneath three calendar years, regardless of SARS-CoV-2 an infection. Older age, male intercourse, and socioeconomic drawback heightened vulnerability, whereas measurable cognitive decline emerged solely when an infection layered neuroinflammatory stress atop socially pushed tissue modifications.
Importantly, these findings must be interpreted within the context of sure limitations, together with the predominance of gentle COVID-19 instances within the cohort and the shortage of pandemic-period psychological well being information.
These outcomes point out that defending mind well being in future crises would require extra than simply an infection management; methods should additionally mitigate the consequences of isolation, unemployment, and healthcare disruptions to stop silent neural ageing and, finally, dementia. Neighborhood outreach and psychological well being care play a vital function in reinforcing resilience.
Journal reference:
- Mohammadi Nejad, A.R., Craig, M., Cox, E.F., Chen, X., Jenkins, R.G., Francis, S., Sotiropoulos, S.N., & Auer, D.P. (2025). Accelerated mind ageing in the course of the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Commun. 16. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61033-4, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-61033-4

